
|
Organizational Hierarchy -Adapting Old Structures to New Challengesby Valdis KrebsWhen change was slow, and the future was pretty much like the present, hierarchical organizations were perfect structures for business and government. The world is no longer predictable, nor are solutions obvious. Old structures are no longer sufficient for new complex challenges. Businesses have noticed the changes and are adapting. From GE's boundaryless organization to Toyota's amazingly flexible supply web, agility and adaptability are the mantra. Unfortunately most governments are not as quick and creative. Instead of the out-of-the-box thinking found increasingly in the business world, governments are busy shuffling boxes on the organization chart. Here is a little "thought experiment" ... Figure 1 below is a sample organization chart of a generic hierarchical organization -- either business or government. Two nodes are connected by a gray link if there is a formal reporting relationship and information flow. The nodes on the bottom row represent sub-organizations, while the top two rows are individuals. 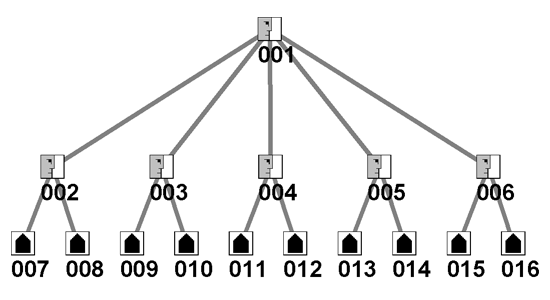
Figure 1 - Original HierarchyAssume the above organizational chart roughly represents the U.S. intelligence community. Node 001 is the President and nodes 007 to 016 are various intelligence agencies. Nodes 002 to 006 are the leaders of those various agencies. Intelligence CzarThe U.S. government is currently facing a dual problem in the intelligence community:
One of the solutions being discussed is adding a new formal position to the intelligence community. This new box would be an 'intelligence czar' to which all other intelligence leaders and their agencies would report. The thinking behind this proposed solution is for there to be one aggregation point for all intelligence. Node 017 in Figure 2 represents this new position. 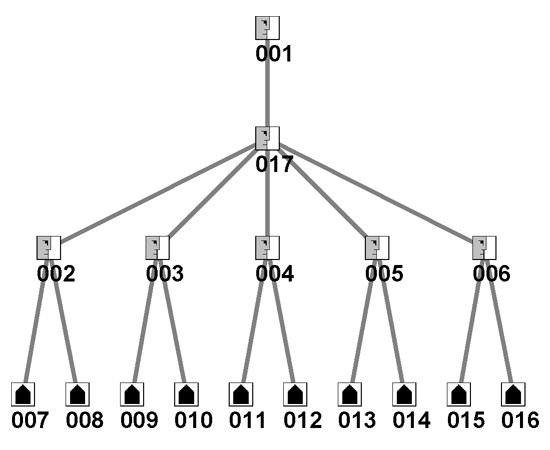
Figure 2 - Adding the Intelligence Czar[017] to Original HierarchyConnecting the Stovepipes / SilosAnother solution to integrate intelligence is to connect the various agencies to each other and start to demand and reward knowledge sharing between them. This does not require a new position. It does require the leaders of the agencies to share knowledge and information and to propogate this new culture down in their organizations where appropriate -- it requires the intelligence community to become a community! This may require new leaders who are open to connecting the stovepipes. Interconnecting the intelligence leadership is displayed by the horizontal green links in Figure 3a. [We moved nodes 003, 004, and 005 so that all green links would be visible -- their new positions on the chart have no further significance.] 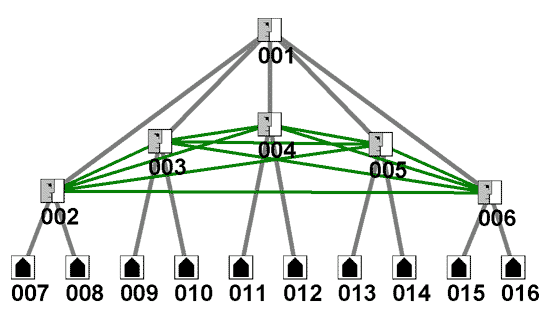
Figure 3a - Horizontal Links added to the Original HierarchyWhich solution is better? The new formal position or the interconnecting of existing positions? It depends on your goal. If you want accountability and budget responsibility then the hierarchy will work. But, if you want a smart, agile learning organization -- able to adapt to a changing enemy -- then the interconnected structure will probably perform better. The interconnected structure spans various organizations with diverse data and perspectives allowing for cross-pollination and learning. Hierarchies vs. Small WorldsWe apply the small-world network metrics of Watts & Strogatz to Figures 1, 2, and 3 above. One of the key metrics in the small-world model is the average path length, for individuals and for the network overall. A good score for an individual means that he/she is close to all of the others in the network -- they can reach others quickly without going through too many intermediaries. A good score for the whole network indicates that everyone can reach everyone else easily and quickly. The shorter the information paths for everyone, the quicker the information arrives and the less distorted it is when it arrives. Another benefit of multiple short paths is that most members of the network have good visibility into what is happening in other parts of the network -- a greater awareness. They have a wide network horizon which is useful for combining key pieces of distributed intelligence. In an environment where it is difficult to distinguish signal from noise, it is important to have many perspectives involved in the sense-making process. Below are the path length metrics for each of the 3 networks above. Two metrics are of high importance. Since the President is the key destination for intelligence, his distance from the rest of the network is critical. The average path length of the whole network is important for sense-making and learning within the group.
Table 1 - Small World MetricsWe can see that Figure 3a is a win-win. Both the President's average path length and the group average path length are reduced. Information flows quicker, with less distortion, and President is more involved. Figure 2 is OK for the overall group, but it increases the President's path length by almost one step. We want our President to be closer to the intelligence community, not further away! Our simple analysis shows that the Intelligence Czar option puts an extra communication burden on the President. Even if the person in this position is top notch, we are still distorting and delaying the information flows by adding this position. The centralized czar does not compute! Figure 3b below gives us insight into why interconnecting the stovepipes is a better option. We redisplay the organization in Figure 3a by 'link patterns' and we see a totally new perspective. Figures 3a and 3b have exactly the same connections -- 3b is the emergent network view of the new organization. By adding the horizontal ties we have transformed a simple hierarchy into an interconnected group. Recent research by psychologist Patrick Laughlin of the University of Illinois shows that groups outperform even the best individuals in decision making. Intelligence information is rarely clear or complete -- a key reason for having many perpsectives and diverse experiences for cross-pollination and sense-making. 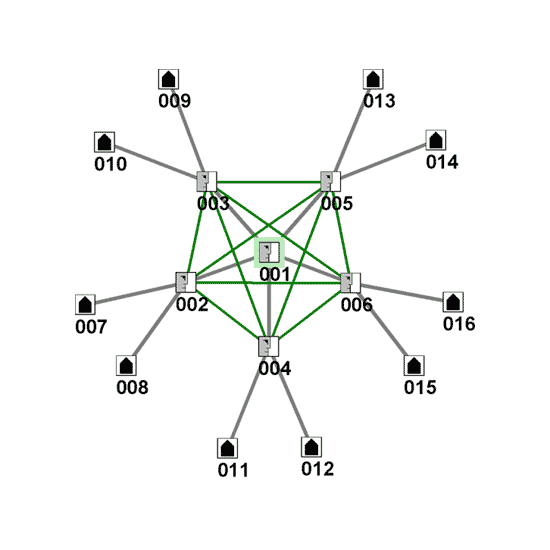
Figure 3b - Emergent Network w/Horizontal Links [Same Links as Figure 3a]Some may ask: What about combining both solutions -- the new position and the horizontal connections? That combination does improve the average path length for the whole group, but the President's path length remains longer [as in Figure 2]. It is not a better choice than Figure 3a/3b. It looks like new connections win out over new nodes! The Report to the President of the United States by The Commission on the Intelligence Capabilities of the United States Regarding Weapons of Mass Destruction came to the same conclusion. Based on their findings: "In sum, today's threats are quick, quiet, and hidden" they concluded, "We need an intelligence community that is truly integrated". Alas, G.W. Bush chose not to improve the overall network, but to add a new position to the hierarchy -- a common approach in the 20th century, and the non-risky choice. Most world leaders are just starting to become network thinkers -- a pattern that will be more common by the end of the 21st century.
|